For immediate release – Researchers from Larkin University successfully published the results of a clinical study of a novel, noninvasive technology for real-time assessment of critical biomedical blood values in PLOS One. The interdisciplinary team lead of biomedical scientists, pharmacists, physicians and respiratory therapists, lead by Dr. Rudi H Ettrich, is a close collaboration of LU’s Colleges of Pharmacy (Dr. Subrata Deb, Dr Prashant Sakharkar, Dr Jayesh Parmar) and Biomedical Sciences (Dr. Sultan Ahmed, Tracy Hurlston) and former LU faculty member Dr Joshua Caballero, now at the University of Georgia.
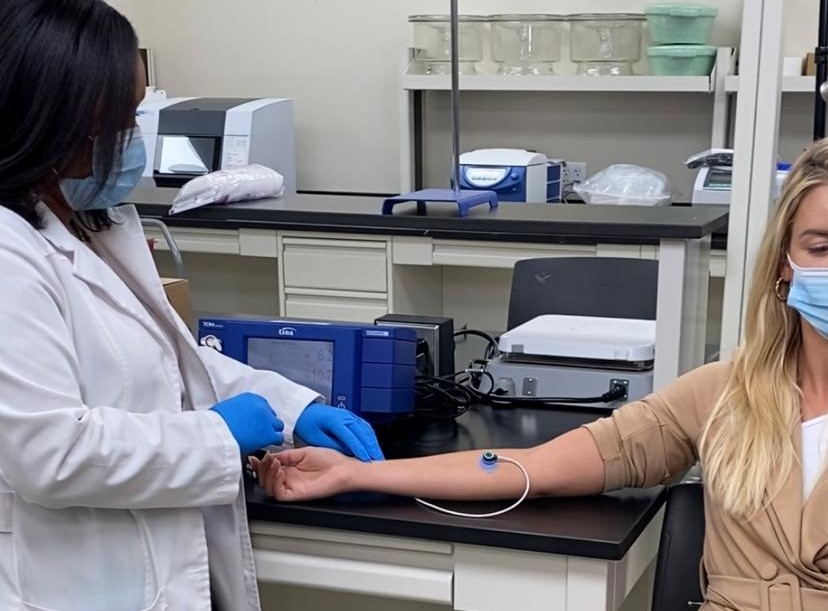
Digital Blood Company in Ft Lauderdale has been founded in 2018 by Slovak inventor Pavel Kazar to develop a novel non-invasive technology to measure critical blood values in real time that has been successfully patented in the US, Canada and Australia. In January 2021 DBC signed a contract with Larkin University to evaluate their new methodology in comparison with a standard point-of-care device in a pilot clinical study. In this study LU researchers investigated the degree of agreement between the two distinct approaches for measuring a set of blood values and to compare comfort levels reported by participants when utilizing these two disparate measurement methods. Radial arterial blood was collected for the comparator analysis using a standard point-of care device. In contrast, the non-invasive proprietary DBC methodology is used to calculate sodium, potassium, chloride, ionized calcium, total carbon dioxide, pH, bicarbonate, and oxygen saturation using four input parameters (temperature, hemoglobin, pO2, and pCO2).
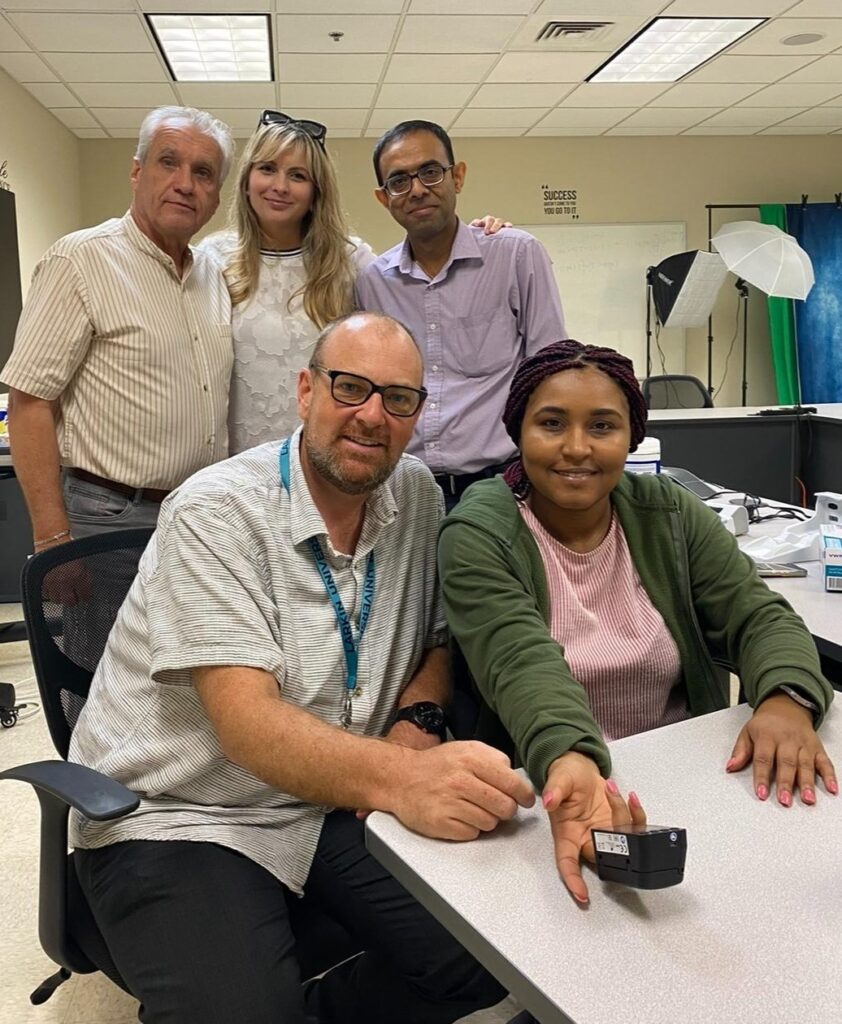

The non-invasive DBC methodology was found to be reliable and robust for most of the measured blood values compared to invasive point-of-care device in healthy participants and does encourage a large-scale clinical study with larger samples and among individuals afflicted with various medical conditions.
Full Citation: Ettrich RH, Caballero J, Sakharkar P, Ahmed S, Hurlston T, Parmar J, Deb S (2024)
Evaluation of agreement between a noninvasive method for real-time measurement of critical blood values with a standard point-of-care device. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0304706. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304706